Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary in the United States
Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary
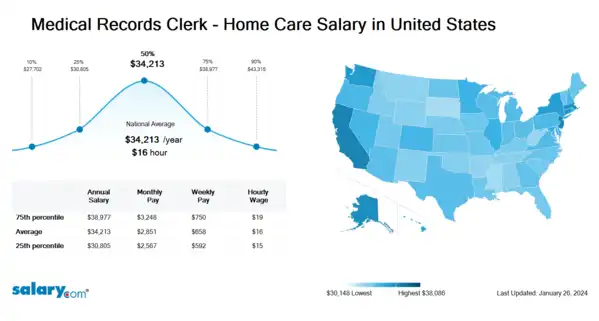
How much does a Medical Records Clerk - Home Care make in the United States? The average Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary in the United States is $34,409 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $30,978 and $39,200. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary | $27,855 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary | $30,978 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary | $34,409 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary | $39,200 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary | $43,562 | US | March 26, 2024 |
Vector Fleet Management - Cincinnati, OH
Metro Lexus: Cleveland, OH - Title Clerk ( Full Time)
Ascent Auto - Cleveland, OH
ExamWorks - Dublin, OH
Health Care Logistics, Inc. - Grove City, OH
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Medical Records Clerk - Home Care need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Confidentiality: The process of and obligation to apply and enforce rules and practices that ensure that specific types of information are accessible only to those authorized to use it.
Health Information Management: Health information management (HIM) is information management applied to health and health care. It is the practice of acquiring, analyzing and protecting digital and traditional medical information vital to providing quality patient care. With the widespread computerization of health records, traditional (paper-based) records are being replaced with electronic health records (EHRs). The tools of health informatics and health information technology are continually improving to bring greater efficiency to information management in the health care sector. Both hospital information systems and Human Resource for Health Information System (HRHIS) are common implementations of HIM. Health information management professionals plan information systems, develop health policy, and identify current and future information needs. In addition, they may apply the science of informatics to the collection, storage, analysis, use, and transmission of information to meet legal, professional, ethical and administrative records-keeping requirements of health care delivery. They work with clinical, epidemiological, demographic, financial, reference, and coded healthcare data. Health information administrators have been described to "play a critical role in the delivery of healthcare in the United States through their focus on the collection, maintenance and use of quality data to support the information-intensive and information-reliant healthcare system".
Home Care: Homecare is health care or supportive care provided by a professional caregiver in the individual home where the patient or client is living, as opposed to care provided in group accommodations like clinics or nursing home.
Job Description for Medical Records Clerk - Home Care
Medical Records Clerk - Home Care organizes, files, and retrieves patient medical records for a home care office. Files various medical documentation, including patient notes, radiology reports, and lab results. Being a Medical Records Clerk - Home Care performs related clerical duties. May be responsible for clerical duties related to patient admission/discharge. Additionally, Medical Records Clerk - Home Care works with both paper-based systems and electronic medical records (EMR). Typically requires a high school diploma or its equivalent. Typically reports to a supervisor or manager. The Medical Records Clerk - Home Care possesses a moderate understanding of general aspects of the job. Works under the close direction of senior personnel in the functional area. May require 0-1 year of general work experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Medical Records Clerk - Home Care.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Medical Records Clerk - Home Care information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Medical Records Clerk - Home Care job openings or enter a new job title here.
What does a Medical Records Clerk - Home Care do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Pay Difference by Location
Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Medical Records Clerk - Home Care, the highest Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary is in Miami, FL, where the Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Medical Records Clerk - Home Care

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Medical Records Clerk | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Medical Records Coding Policy Administrator | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Medical Records Coding Technician II | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Medical Records Research Coordinator | Experience 0 - 1 | EducationAssociates | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Medical Records Senior Supervisor | Experience 3 - 5 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Medical Records Clerk - Home Care
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary of your education level.
- Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Medical Records Clerk - Home Care Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Healthcare - Practitioners Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Medical Records Clerk - Home Care
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Medical Records Clerk - Home Care salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Medical Records Clerk - Home Care, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Medical Records Clerk - Home Care: HIPAA Compliance, Electronic health records (EHR) Software, Data Entry-Keyboarding, Medical Record Keeping ...More
Recently searched related titles: Web Marketing Assistant, Medical Records Tech
Salary estimation for Medical Records Clerk - Home Care at companies like : Georgetown International Investmnt Bnkng Srvcs, Insurance: Kendall Toyota of Anchorage Insurance, PHH Holdings Inc
Jobs with a similar salary range to Medical Records Clerk - Home Care : Insurance Recovery Specialist