Rigger Salary in the United States
Rigger Salary
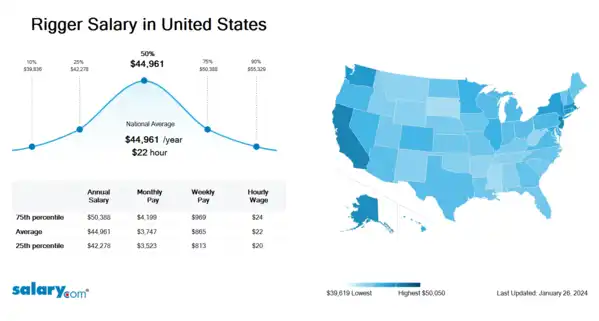
How much does a Rigger make in the United States? The average Rigger salary in the United States is $45,134 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $42,442 and $50,582. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Rigger Salary | $39,990 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Rigger Salary | $42,442 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Rigger Salary | $45,134 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Rigger Salary | $50,582 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Rigger Salary | $55,542 | US | March 26, 2024 |
SHOEMAKER RIGGING AND TRANSPORT LLC - Akron, OH
Plants and Goodwin, Inc. - Cambridge, OH
PRESTIGE AUDIO VISUAL INC - Cincinnati, OH
Cleveland Marine - Cleveland, OH
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Rigger need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Commitment: An agreement or pledge to do something in the future a commitment to improve conditions at the prison especially : an engagement to assume a financial obligation at a future date.
Futures: Futures are derivative financial contracts obligating the buyer to purchase an asset or the seller to sell an asset at a predetermined future date and set price.
Plant Maintenance: Keeping all plant assets and facilities in good operating conditions to minimize downtime and achieve production objectives.
Job Description for Rigger
Rigger facilitates the movement and positioning of heavy equipment, materials and cargo. Sets up rigging, slings, pulleys, winches, dollies and ropes to safely maneuver loads. Being a Rigger coordinates moving activities with others using hand or other signals. Requires a high school diploma or its equivalent. Additionally, Rigger may be required to complete an apprenticeship and/or formal training in area of specialty. Requires 2-4 years of experience in the field or in a related area. Familiar with standard concepts, practices, and procedures within a particular field. Relies on experience and judgment to plan and accomplish goals. Performs a variety of tasks. Works under general supervision; typically reports to a supervisor or manager. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Rigger information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Rigger job openings or enter a new job title here.
What does a Rigger do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Rigger Pay Difference by Location
Rigger salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Rigger, the highest Rigger salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Rigger salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Rigger salary is in Miami, FL, where the Rigger salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Rigger

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Choke Setter | Experience | Education | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Rigger
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Rigger salary of your education level.
Rigger Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Rigger salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Skilled and Trades Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Rigger
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Rigger salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Rigger salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Rigger, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Salary estimation for Rigger at companies like : Exostone Group LLC, Bronson Methodist Hospital, Amy Gould Architect AIA