Model Maker Salary in the United States
Model Maker Salary
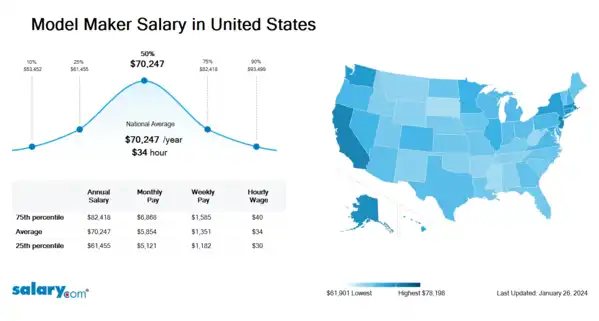
How much does a Model Maker make in the United States? The average Model Maker salary in the United States is $71,044 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $62,152 and $83,353. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Model Maker Salary | $54,057 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Model Maker Salary | $62,152 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Model Maker Salary | $71,044 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Model Maker Salary | $83,353 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Model Maker Salary | $94,560 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Model Maker need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Problem Solving: Analyzing and identifying the root cause of problems and applying critical thinking skills to solve problems.
Agile Methodology: The Agile methodology is a way to manage a project by breaking it up into several phases. The goal of Agile is to produce shorter development cycles and more frequent product releases than traditional waterfall project management.
Functional Requirements: In software engineering and systems engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a system or its component, where a function is described as a specification of behavior between outputs and inputs. Functional requirements may involve calculations, technical details, data manipulation and processing, and other specific functionality that define what a system is supposed to accomplish. Behavioral requirements describe all the cases where the system uses the functional requirements, these are captured in use cases. Functional requirements are supported by non-functional requirements (also known as "quality requirements"), which impose constraints on the design or implementation (such as performance requirements, security, or reliability). Generally, functional requirements are expressed in the form "system must do <requirement>," while non-functional requirements take the form "system shall be <requirement>." The plan for implementing functional requirements is detailed in the system design, whereas non-functional requirements are detailed in the system architecture.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Model Maker
Model Maker creates, designs, and constructs tools and parts in a variety of materials such as wood and plastic. Uses blueprints, drawings, and/or CAD designs to create models according to established specifications. Being a Model Maker may perform minor repair on model making machinery. Requires a high school diploma. Additionally, Model Maker typically reports to a supervisor. The Model Maker works under moderate supervision. Gaining or has attained full proficiency in a specific area of discipline. To be a Model Maker typically requires 1-3 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Model Maker information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Model Maker job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Model Maker
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Model Maker, the first career path typically progresses to Model Maker, Sr..
What does a Model Maker do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Model Maker Pay Difference by Location
Model Maker salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Model Maker, the highest Model Maker salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Model Maker salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Model Maker salary is in Miami, FL, where the Model Maker salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Model Maker

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Compounder | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Compounder, Sr. | Experience 3 - 5 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Model Maker, Sr. | Experience 3 - 5 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Quality Assurance Engineering Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Sample Maker | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Model Maker
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Model Maker salary of your education level.
Model Maker Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Model Maker salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Aerospace and Defense Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Model Maker
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Model Maker salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Model Maker salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Model Maker, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Model Maker: 3D Modeling, Product Specifications, 3D CAD, Reading Blueprints/Diagrams ...More
Recently searched related titles: 3D Modeler, Clay Modeler
Recently searched related titles: Variable Compensation Analyst
Jobs with a similar salary range to Model Maker : Model
Salary estimation for Model Maker at companies like : Vnrsmc Holdings LLC, UConn Early College Experience, First Union Commercial Mortgage Securities Inc Ser 1997 C..https
Jobs with a similar salary range to Model Maker : Marker Maker, Mold Designer, Market Maker