Physician - Urology Salary in the United States
Physician - Urology Salary
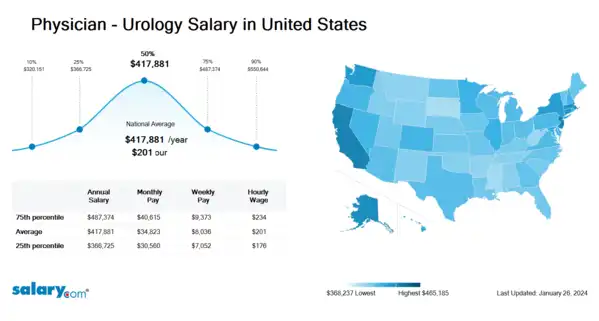
How much does a Physician - Urology make in the United States? The average Physician - Urology salary in the United States is $419,622 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $368,247 and $489,394. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Physician - Urology Salary | $321,472 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Physician - Urology Salary | $368,247 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Physician - Urology Salary | $419,622 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Physician - Urology Salary | $489,394 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Physician - Urology Salary | $552,918 | US | March 26, 2024 |
Physician Urology - Competitive Salary
Wapiti Medical Staffing - Ashtabula, OH
Physician Urology - Competitive Salary
RecruitWell - Ashtabula, OH
Physician Urology - Competitive Salary
TinkBird Healthcare Staffing / Locum Tenens & Perm - Ashtabula, OH
Physician Urology - Competitive Salary
MedExcellence - Ashtabula, OH
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Physician - Urology need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Leadership: Knowledge of and ability to employ effective strategies that motivate and guide other members within our business to achieve optimum results.
Medical Education: Medical education is a course of study directed toward imparting knowledge and skills required for the prevention and treatment of diseases to persons seeking to become physicians.
Pediatric: Pediatrics is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults.
Job Description for Physician - Urology
Physician - Urology examines and diagnoses disorders and diseases of the genitourinary tract and organs. Consults with patients to determine the appropriate course of treatment. Being a Physician - Urology recommends and orders tests to determine extent of illness or help diagnose condition. Requires a MD degree from an accredited school. Additionally, Physician - Urology requires a valid state license to practice. May report to a medical director. Physician - Urology's years of experience requirement may be unspecified. Certification and/or licensing in the position's specialty is the main requirement. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Physician - Urology.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Physician - Urology information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Physician - Urology job openings or enter a new job title here.
What does a Physician - Urology do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Physician - Urology Pay Difference by Location
Physician - Urology salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Physician - Urology, the highest Physician - Urology salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Physician - Urology salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Physician - Urology salary is in Miami, FL, where the Physician - Urology salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Physician - Urology

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Physician - Hospitalist | Experience | EducationMD | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Physician Assistant - Medical | Experience | EducationMasters | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Physician Assistant - Orthopedics | Experience | EducationMasters | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Physician Assistant - Primary Care | Experience | EducationMasters | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Physician Assistant - Specialty | Experience | EducationMasters | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Physician - Urology
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Physician - Urology salary of your education level.
Physician - Urology Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Physician - Urology salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Healthcare - Practitioners Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Physician - Urology
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Physician - Urology salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Physician - Urology salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Physician - Urology, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Physician - Urology: Electronic health records (EHR) Software, E-Prescribing Software, Diagnosis and Treatment Planning, Medical Specialty: Urology ...More
Jobs with a similar salary range to Physician - Urology : Urology Physician Assistant
Salary estimation for Physician - Urology at companies like : Grindel eV, Student Services Center, GreenLight Bionics