Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary in the United States
Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary
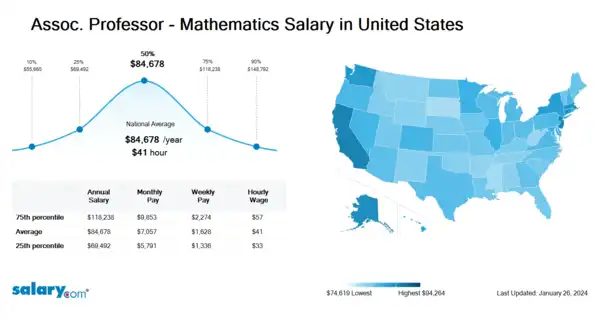
How much does an Assoc. Professor - Mathematics make in the United States? The average Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary in the United States is $85,008 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $69,763 and $118,698. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary | $55,884 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary | $69,763 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary | $85,008 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary | $118,698 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary | $149,372 | US | March 26, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does an Assoc. Professor - Mathematics need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Commitment: An agreement or pledge to do something in the future a commitment to improve conditions at the prison especially : an engagement to assume a financial obligation at a future date.
Blended Learning: Blended learning is an approach to education that combines online educational materials and opportunities for interaction online with traditional place-based classroom methods. It requires the physical presence of both teacher and student, with some elements of student control over time, place, path, or pace. While students still attend "brick-and-mortar" schools with a teacher present, face-to-face classroom practices are combined with computer-mediated activities regarding content and delivery. Blended learning is also used in professional development and training settings. Blended learning is highly context-dependent therefore a universal conception of it is hard to come by. Some reports have claimed that a lack of consensus on a hard definition of blended learning had led to difficulties in research on its effectiveness. However, a 2015 meta-analysis that historically looked back at a comprehensive review of evidence-based research studies around blended learning, found commonalities in defining that blended learning was "considered a combination of traditional f2f [face to face] modes of instruction with online modes of learning, drawing on technology-mediated instruction, where all participants in the learning process are separated by distance some of the time." This report also found that all of these evidence-based studies concluded that student achievement was higher in blended learning experiences when compared to either fully online or fully face-to-face learning experiences.
Data Analysis: Data analysis is a process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches, encompassing diverse techniques under a variety of names, and is used in different business, science, and social science domains. In today's business world, data analysis plays a role in making decisions more scientific and helping businesses operate more effectively. Data mining is a particular data analysis technique that focuses on modeling and knowledge discovery for predictive rather than purely descriptive purposes, while business intelligence covers data analysis that relies heavily on aggregation, focusing mainly on business information. In statistical applications, data analysis can be divided into descriptive statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA), and confirmatory data analysis (CDA). EDA focuses on discovering new features in the data while CDA focuses on confirming or falsifying existing hypotheses. Predictive analytics focuses on application of statistical models for predictive forecasting or classification, while text analytics applies statistical, linguistic, and structural techniques to extract and classify information from textual sources, a species of unstructured data. All of the above are varieties of data analysis.
Job Description for Assoc. Professor - Mathematics
Assoc. Professor - Mathematics teaches courses in the discipline area of mathematics. Develops and designs curriculum plans to foster student learning, stimulate class discussions, and ensures student engagement. Being an Assoc. Professor - Mathematics provides tutoring and academic counseling to students, maintains classes related records, and assesses student coursework. Collaborates and supports colleagues regarding research interests and co-curricular activities. Additionally, Assoc. Professor - Mathematics typically reports to a department head. Requires a PhD or terminal degree appropriate to the field. Has considerable experience and is qualified to teach at undergraduate and graduate levels and conducts research and case studies in field of interest and may publish findings in trade journals or textbooks. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Assoc. Professor - Mathematics.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Assoc. Professor - Mathematics information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Assoc. Professor - Mathematics job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Assoc. Professor - Mathematics
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Assoc. Professor - Mathematics, the first career path typically progresses to Professor - Architecture.
The second career path typically progresses to Professor - Biology.
The third career path typically progresses to Professor - Chemical Engineering.
Additionally, the fourth career path typically progresses to Professor - Civil Engineering.
What does an Assoc. Professor - Mathematics do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Pay Difference by Location
Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Assoc. Professor - Mathematics, the highest Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary is in Miami, FL, where the Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Assoc. Professor - Mathematics

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Associate Dean of Mathematics | Experience | EducationAdvanced | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Asst. Professor - Mathematics | Experience | EducationPh. D | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Dean of Mathematics | Experience | EducationAdvanced | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Instructor - Mathematics | Experience | EducationMasters | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Professor - English | Experience | EducationPh. D | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Assoc. Professor - Mathematics
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary of your education level.
Assoc. Professor - Mathematics Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Education Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Assoc. Professor - Mathematics
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Assoc. Professor - Mathematics salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for an Assoc. Professor - Mathematics, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Assoc. Professor - Mathematics: Develop Courses, Academic Advising, Monitor Student Performance, Academic Research ...More
Recently searched related titles: Analytics Professional
Salary estimation for Assoc. Professor - Mathematics at companies like : Top Tier Hospitality, Pruitt Communications Inc, University of Colorado ARTS Parkside Clinic
Jobs with a similar salary range to Assoc. Professor - Mathematics : Christian School Principal, Community Development, Economic Advisor