Product Design Director Salary in the United States
Product Design Director Salary
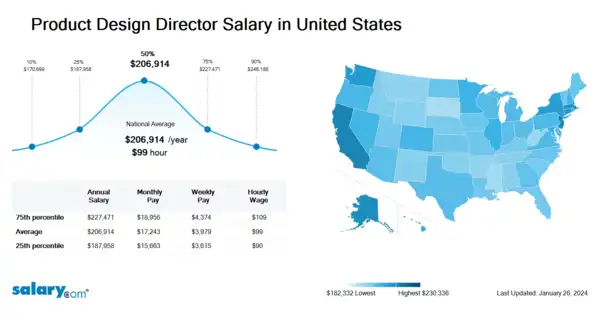
How much does a Product Design Director make in the United States? The average Product Design Director salary in the United States is $208,175 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $189,104 and $228,861. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Product Design Director Salary | $171,741 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Product Design Director Salary | $189,104 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Product Design Director Salary | $208,175 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Product Design Director Salary | $228,861 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Product Design Director Salary | $247,695 | US | March 26, 2024 |
Manager of Design Curator Services
Koroseal Interior Products - Akron, OH
YMCA of Central Stark County - Canton, OH
Director Quality Assurance and Regulatory Affairs
Gateway Recruiting, INC. - Cincinnati, OH
(Apparel) Product Design Manager
National Safety Apparel - Cleveland, OH
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Product Design Director need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Leadership: Knowledge of and ability to employ effective strategies that motivate and guide other members within our business to achieve optimum results.
Design Thinking: Developing software solutions to understand and target customer needs in a repetitive process.
Typography: Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable, and appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line-spacing (leading), and letter-spacing (tracking), and adjusting the space between pairs of letters (kerning). The term typography is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as a decorative device, unrelated to communication of information. Typography is the work of typesetters (also known as compositors), typographers, graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, graffiti artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers, and symbols for publication, display, or distribution, from clerical workers and newsletter writers to anyone self-publishing materials. Until the Digital Age, typography was a specialized occupation. Digitization opened up typography to new generations of previously unrelated designers and lay users. As the capability to create typography has become ubiquitous, the application of principles and best practices developed over generations of skilled workers and professionals has diminished. So at a time when scientific techniques can support the proven traditions (e.g., greater legibility with the use of serifs, upper and lower case, contrast, etc.) through understanding the limitations of human vision, typography as often encountered may fail to achieve its principal objective: effective communication.
Job Description for Product Design Director
Product Design Director oversees the implementation of product design and development policies, objectives, and initiatives. Directs the design, development, and enhancement of new and existing products/product lines. Being a Product Design Director evaluates and ensures design feasibility and design optimization. Helps facilitate project milestones and determination of project timelines. Additionally, Product Design Director evaluates issues and provides resolution and communicates and influences top management. Requires a bachelor's degree. Typically reports to top management. The Product Design Director manages a departmental sub-function within a broader departmental function. Creates functional strategies and specific objectives for the sub-function and develops budgets/policies/procedures to support the functional infrastructure. To be a Product Design Director typically requires 5+ years of managerial experience. Deep knowledge of the managed sub-function and solid knowledge of the overall departmental function. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Product Design Director.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Product Design Director information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Product Design Director job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Product Design Director
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Product Design Director, the first career path typically progresses to Top Product Design Executive.
What does a Product Design Director do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Product Design Director Pay Difference by Location
Product Design Director salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Product Design Director, the highest Product Design Director salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Product Design Director salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Product Design Director salary is in Miami, FL, where the Product Design Director salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Product Design Director

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Product Design Engineer I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Product Design Engineer II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Product Design Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Product Design Engineer IV | Experience 7 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Product Design Engineer V | Experience 10 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Product Design Director
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Product Design Director salary of your education level.
- Product Design Director Salaries with No Diploma
- Product Design Director Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Product Design Director Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Product Design Director Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Product Design Director Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Product Design Director Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Product Design Director Salary by Global Country
Product Design Director salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Product Design Director salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Product Design Director salary of the other country.
Product Design Director Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Product Design Director salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Engineering Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Product Design Director
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Product Design Director salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Product Design Director salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Product Design Director, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Product Design Director: Feasibility Study, Product Innovation, CAD Software, Product Planning ...More
Recently searched related titles: Head Of Product Design, Director Of Product Engineering, Director Of Product Design
Jobs with a similar salary range to Product Design Director : Associate Design Director, Industrial Design Director, Design Principal, Director of Engineering Product Management, Director of Product
Salary estimation for Product Design Director at companies like : MyersCo Builders LLC, Vysr Inc, Proseed Property Ltd