Video Editor Salary in the United States
Video Editor Salary
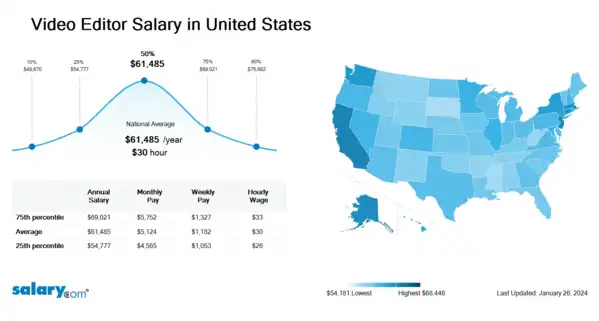
How much does a Video Editor make in the United States? The average Video Editor salary in the United States is $62,300 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $55,499 and $69,931. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Video Editor Salary | $49,308 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Video Editor Salary | $55,499 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Video Editor Salary | $62,300 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Video Editor Salary | $69,931 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Video Editor Salary | $76,878 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Video Editor need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Storytelling: Planning, creating and presenting stories or narratives to achieve diverse personal and business goals.
Animation: Animation is a method in which pictures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most animations are made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Computer animation can be very detailed 3D animation, while 2D computer animation can be used for stylistic reasons, low bandwidth or faster real-time renderings. Other common animation methods apply a stop motion technique to two and three-dimensional objects like paper cutouts, puppets or clay figures. Commonly the effect of animation is achieved by a rapid succession of sequential images that minimally differ from each other. The illusion—as in motion pictures in general—is thought to rely on the phi phenomenon and beta movement, but the exact causes are still uncertain. Analog mechanical animation media that rely on the rapid display of sequential images include the phénakisticope, zoetrope, flip book, praxinoscope and film. Television and video are popular electronic animation media that originally were analog and now operate digitally. For display on the computer, techniques like animated GIF and Flash animation were developed.
Professional Development: Professional development refers to continuing education and career training after a person has entered the workforce in order to help them develop new skills, stay up-to-date on current trends, and advance their career.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Video Editor
Video Editor edits video footage to desired length and format, creates motion graphics, and completes color corrections. Mixes and masters audio. Being a Video Editor encodes final videos to desired size and format. Archives and stores all files, footage, graphics, and audio. Additionally, Video Editor proficient using production and editing software including Adobe Creative suite and other specialized editing tools. Typically requires a bachelor's degree. Typically reports to a supervisor or manager. The Video Editor work is closely managed. Works on projects/matters of limited complexity in a support role. To be a Video Editor typically requires 0-2 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Video Editor information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Video Editor job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Video Editor
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Video Editor, the upper level is Senior Producer and then progresses to Creative Production Manager.
What does a Video Editor do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Video Editor Pay Difference by Location
Video Editor salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Video Editor, the highest Video Editor salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Video Editor salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Video Editor salary is in Miami, FL, where the Video Editor salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Video Editor

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Communications Editor I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor IV | Experience 7 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Editor I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Video Editor
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Video Editor salary of your education level.
- Video Editor Salaries with No Diploma
- Video Editor Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Video Editor Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Video Editor Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Video Editor Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Video Editor Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Video Editor Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Video Editor salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Arts and Entertainment Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Video Editor
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Video Editor salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Video Editor salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Video Editor, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Video Editor: Adobe Creative Suite, Video Editing, Color Management, Audio Mixing ...More
Recently searched related titles: Audio Or Video Production Or Recording, Assistant Video Editor, Movie Trailer Editor
Recently searched related titles: Senior Video Editor, Document Curative Specialist
Jobs with a similar salary range to Video Editor : Assistant Film Editor, Digital Video Editor
Salary estimation for Video Editor at companies like : Chevrolet Silverado 1500 2WD, RavnAir Group, Bank of America Plaza
Jobs with a similar salary range to Video Editor : Grant Reviewer, Podcast Editor, Fidelity Financial Representative