Communications Editor III Salary in the United States
Communications Editor III Salary
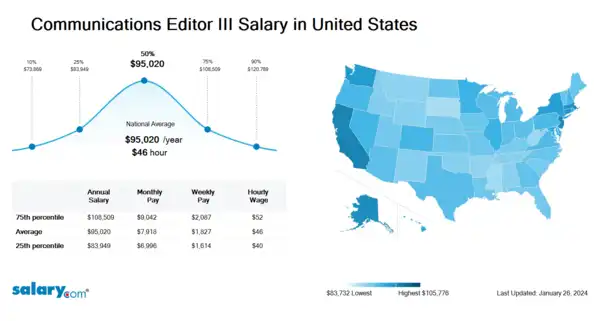
How much does a Communications Editor III make in the United States? The average Communications Editor III salary in the United States is $96,282 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $85,059 and $109,949. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Communications Editor III Salary | $74,841 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Communications Editor III Salary | $85,059 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Communications Editor III Salary | $96,282 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Communications Editor III Salary | $109,949 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Communications Editor III Salary | $122,392 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Communications Editor III need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Presentation: Presentation conveys information from a speaker to an audience. Presentations are typically demonstrations, introduction, lecture, or speech meant to inform, persuade, inspire, motivate, build goodwill, or present a new idea/product.
Digital Marketing: Digital marketing is the marketing of products or services using digital technologies, mainly on the Internet, but also including mobile phones, display advertising, and any other digital medium. Digital marketing's development since the 1990s and 2000s has changed the way brands and businesses use technology for marketing. As digital platforms are increasingly incorporated into marketing plans and everyday life, and as people use digital devices instead of visiting physical shops, digital marketing campaigns are becoming more prevalent and efficient. Digital marketing methods such as search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, influencer marketing, content automation, campaign marketing, data-driven marketing, e-commerce marketing, social media marketing, social media optimization, e-mail direct marketing, Display advertising, e–books, and optical disks and games are becoming more common in our advancing technology. In fact, digital marketing now extends to non-Internet channels that provide digital media, such as mobile phones (SMS and MMS), callback, and on-hold mobile ring tones. In essence, this extension to non-Internet channels helps to differentiate digital marketing from online marketing, another catch-all term for the marketing methods mentioned above, which strictly occur online.
Content Creation: Content creation is the contribution of information to any media and most especially to digital media for an end-user/audience in specific contexts. Content is "something that is to be expressed through some medium, as speech, writing or any of various arts" for self-expression, distribution, marketing and/or publication. Typical forms of content creation include maintaining and updating web sites, blogging, photography, videography, online commentary, the maintenance of social media accounts, and editing and distribution of digital media. A Pew survey described content creation as the creation of "the material people contribute to the online world."
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Communications Editor III
Communications Editor III writes, prepares, and/or reviews content to be used in company publications. Coordinates the preparation of company publications and articles with various departments. Being a Communications Editor III reviews artwork and verifies facts. Ensures all work follows editorial policies and standards. Additionally, Communications Editor III maintains company's identity, design standards, and policies. May provide guidance to lower-level staff. Requires a bachelor's degree. Typically reports to a supervisor or manager. The Communications Editor III work is generally independent and collaborative in nature. Contributes to moderately complex aspects of a project. To be a Communications Editor III typically requires 4-7 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Communications Editor III.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Communications Editor III information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Communications Editor III job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Communications Editor III
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Communications Editor III, the upper level is Communications Editor IV and then progresses to Communications Editor Supervisor.
What does a Communications Editor III do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Communications Editor III Pay Difference by Location
Communications Editor III salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Communications Editor III, the highest Communications Editor III salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Communications Editor III salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Communications Editor III salary is in Miami, FL, where the Communications Editor III salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Communications Editor III

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Communications Editor I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor IV | Experience 7 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Communications Editor Supervisor | Experience 3 - 5 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Communications Editor III
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Communications Editor III salary of your education level.
Communications Editor III Salary by Global Country
Communications Editor III salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Communications Editor III salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Communications Editor III salary of the other country.
Communications Editor III Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Communications Editor III salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Media - Print Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Communications Editor III
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Communications Editor III salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Communications Editor III salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Communications Editor III, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Communications Editor III: Content Research, Proofreading, Brand Management, Copyediting ...More
Recently searched related titles: Mass Communication
Recently searched related titles: Junior IT Manager, Senior Communications Coordinator, Federal Project Manager
Jobs with a similar salary range to Communications Editor III : Assignment Editor, Production Editor, Research Editor
Salary estimation for Communications Editor III at companies like : Converse County School District, Ball State FCU, Assurance Title & Abstract Inc
Jobs with a similar salary range to Communications Editor III : Compositor, Administrative Staff Analyst, Edison Engineer