Industrial Engineer V Salary in the United States
Industrial Engineer V Salary
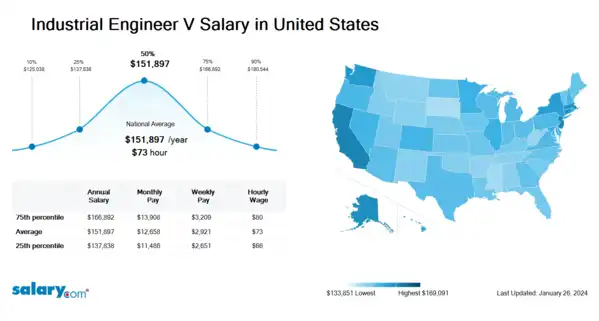
How much does an Industrial Engineer V make in the United States? The average Industrial Engineer V salary in the United States is $156,248 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $140,969 and $172,418. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Industrial Engineer V Salary | $127,057 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Industrial Engineer V Salary | $140,969 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Industrial Engineer V Salary | $156,248 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Industrial Engineer V Salary | $172,418 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Industrial Engineer V Salary | $187,140 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does an Industrial Engineer V need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Analysis: Analysis is the process of considering something carefully or using statistical methods in order to understand it or explain it.
Lean Manufacturing: Lean manufacturing or lean production is a systematic method originating in the Japanese manufacturing industry for the minimization of waste (無駄, muda) within a manufacturing system without sacrificing productivity, which can cause problems. Lean also takes into account waste created through overburden (無理, muri) and unevenness in work loads (斑, mura). Working from the perspective of the client who consumes a product or service, "value" is any action or process that a customer would be willing to pay for.[citation needed] Lean manufacturing attempts to make obvious what adds value, through reducing everything else (because it is not adding value). This management philosophy is derived mostly from the Toyota Production System (TPS) and identified as "lean" only in the 1990s.[page needed], TPS is renowned for its focus on reduction of the original Toyota seven wastes to improve overall customer value, but there are varying perspectives on how this is best achieved. The steady growth of Toyota, from a small company to the world's largest automaker, has focused attention on how it has achieved this success.
Production Schedule: Is a project plan of how the production budget will be spent over a given timescale, for every phase of a business project.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Industrial Engineer V
Industrial Engineer V designs equipment or machine layout to coordinate activities and production planning to ensure products meet quality standards while minimizing production problems and costs. Develops and maintains manufacturing routes for maximizing space, efficiency, and effectiveness. Being an Industrial Engineer V ensures compliance with industry safety and design standards and guidelines. Typically requires a bachelor's degree of engineering. Additionally, Industrial Engineer V typically reports to a manager. The Industrial Engineer V works on advanced, complex technical projects or business issues requiring state of the art technical or industry knowledge. Works autonomously. Goals are generally communicated in solution or project goal terms. May provide a leadership role for the work group through knowledge in the area of specialization. To be an Industrial Engineer V typically requires 10+ years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Industrial Engineer V.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Industrial Engineer V information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Industrial Engineer V job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Industrial Engineer V
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Industrial Engineer V, the first career path typically progresses to Industrial Engineering Manager.
What does an Industrial Engineer V do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Industrial Engineer V Pay Difference by Location
Industrial Engineer V salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Industrial Engineer V, the highest Industrial Engineer V salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Industrial Engineer V salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Industrial Engineer V salary is in Miami, FL, where the Industrial Engineer V salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Industrial Engineer V

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Chemical Process Engineer V | Experience 10 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Civil Engineer V | Experience 10 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Control & Instrument Engineer V | Experience 10 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Engineer V | Experience 10 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Industrial Engineer I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Industrial Engineer V
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Industrial Engineer V salary of your education level.
Industrial Engineer V Salary by Global Country
Industrial Engineer V salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Industrial Engineer V salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Industrial Engineer V salary of the other country.
Industrial Engineer V Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Industrial Engineer V salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Engineering Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Industrial Engineer V
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Industrial Engineer V salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Industrial Engineer V salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for an Industrial Engineer V, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Industrial Engineer V: Lean Manufacturing, Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) Software, Process Engineering, Production Engineering ...More
Recently searched related titles: Senior Claim Counsel
Jobs with a similar salary range to Industrial Engineer V : Lead Industrial Engineer
Salary estimation for Industrial Engineer V at companies like : Babylon Products Inc, 13612994 Centers for Autism Treatment Inc, Prevent Blindness Of Ne
Jobs with a similar salary range to Industrial Engineer V : Executive General Adjuster, Chief Consultant