Polysomnographic Technician Salary in the United States
Polysomnographic Technician Salary
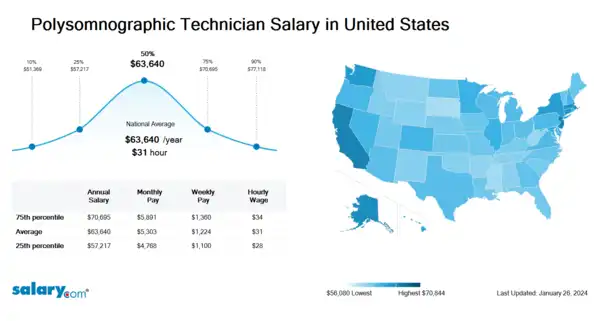
How much does a Polysomnographic Technician make in the United States? The average Polysomnographic Technician salary in the United States is $64,220 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $57,735 and $71,338. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Polysomnographic Technician Salary | $51,831 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Polysomnographic Technician Salary | $57,735 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Polysomnographic Technician Salary | $64,220 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Polysomnographic Technician Salary | $71,338 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Polysomnographic Technician Salary | $77,819 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Polysomnographic Technician need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Analysis: Analysis is the process of considering something carefully or using statistical methods in order to understand it or explain it.
CPR: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) combines rescue breathing (mouth-to-mouth) and chest compressions to temporarily pump enough blood to the brain until specialized treatment is available.
Infection Control: Infection control is the discipline concerned with preventing nosocomial or healthcare-associated infection, a practical (rather than academic) sub-discipline of epidemiology. It is an essential, though often underrecognized and undersupported, part of the infrastructure of health care. Infection control and hospital epidemiology are akin to public health practice, practiced within the confines of a particular health-care delivery system rather than directed at society as a whole. Anti-infective agents include antibiotics, antibacterials, antifungals, antivirals and antiprotozoals. Infection control addresses factors related to the spread of infections within the healthcare setting (whether patient-to-patient, from patients to staff and from staff to patients, or among-staff), including prevention (via hand hygiene/hand washing, cleaning/disinfection/sterilization, vaccination, surveillance), monitoring/investigation of demonstrated or suspected spread of infection within a particular health-care setting (surveillance and outbreak investigation), and management (interruption of outbreaks). It is on this basis that the common title being adopted within health care is "infection prevention and control."
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Polysomnographic Technician
Polysomnographic Technician under the direction of a physician, administers various sleep studies in order to diagnose the type and extent of sleep disorders. Performs routine patient assessments, scores sleep records, documents other test results, and collects and transmits biological specimens for analysis. Being a Polysomnographic Technician typically requires an associate degree or its equivalent and certification as a Polysomnographic Technician. Typically reports to a supervisor or manager. Polysomnographic Technician's years of experience requirement may be unspecified. Certification and/or licensing in the position's specialty is the main requirement. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Polysomnographic Technician.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Polysomnographic Technician information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Polysomnographic Technician job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Polysomnographic Technician
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Polysomnographic Technician, the first career path typically starts with an Audiology Technician position, and then Audiology and Speech Therapy Manager.
The second career path typically progresses to Endoscopy Technician.
Additionally, the third career path typically progresses to Sleep Center Manager.
What does a Polysomnographic Technician do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Polysomnographic Technician Pay Difference by Location
Polysomnographic Technician salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Polysomnographic Technician, the highest Polysomnographic Technician salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Polysomnographic Technician salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Polysomnographic Technician salary is in Miami, FL, where the Polysomnographic Technician salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Polysomnographic Technician

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Calibration Technician I | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Calibration Technician II | Experience 3 - 5 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Calibration Technician III | Experience 5 - 7 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Instrument Technician II | Experience 3 - 5 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Production Technician I | Experience 0 - 1 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Polysomnographic Technician
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Polysomnographic Technician salary of your education level.
Polysomnographic Technician Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Polysomnographic Technician salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Healthcare - Technicians Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Polysomnographic Technician
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Polysomnographic Technician salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Polysomnographic Technician salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Polysomnographic Technician, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Polysomnographic Technician: Physician Support, Patient Monitoring, Perform Diagnostic Tests, Specialized Medical Equipment Operation ...More
Recently searched related titles: Public Auditor, Bank Compliance Officer, Polysomnographic Tech
Jobs with a similar salary range to Polysomnographic Technician : Management Coordinator, Sleep Expert, Registered Polysomnographer
Salary estimation for Polysomnographic Technician at companies like : Knj Aircraft, Methodist Sugar Land Hospital, antgab will holdings LLC
Jobs with a similar salary range to Polysomnographic Technician : Investment Banking Intern, Sleep Tech, Rpsgt