Engineer III Salary in the United States
Engineer III Salary
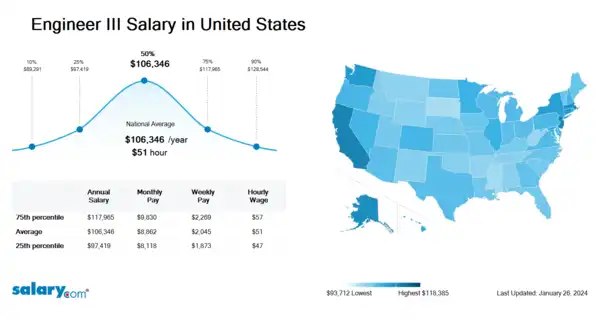
How much does an Engineer III make in the United States? The average Engineer III salary in the United States is $106,875 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $97,903 and $118,550. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Engineer III Salary | $89,735 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Engineer III Salary | $97,903 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Engineer III Salary | $106,875 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Engineer III Salary | $118,550 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Engineer III Salary | $129,180 | US | March 26, 2024 |
Civil Engineer 3 - 5 years w/PE
INTEGRITY FEDERAL SERVICES, INC. - Beachwood, OH
OSIS - Cincinnati, OH
Municipal - Project Engineer 3
Gertsburg Licata Co., LPA - Cincinnati, OH
Preformed Line Products - Cleveland, OH
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does an Engineer III need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Analysis: Analysis is the process of considering something carefully or using statistical methods in order to understand it or explain it.
Carpentry: Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenters traditionally worked with natural wood and did the rougher work such as framing, but today many other materials are also used and sometimes the finer trades of cabinetmaking and furniture building are considered carpentry. In the United States, 98.5% of carpenters are male, and it was the fourth most male-dominated occupation in the country in 1999. In 2006 in the United States, there were about 1.5 million carpentry positions. Carpenters are usually the first tradesmen on a job and the last to leave. Carpenters normally framed post-and-beam buildings until the end of the 19th century; now this old fashioned carpentry is called timber framing. Carpenters learn this trade by being employed through an apprenticeship training—normally 4 years—and qualify by successfully completing that country's competence test in places such as the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Australia and South Africa. It is also common that the skill can be learned by gaining work experience other than a formal training program, which may be the case in many places.
Java: Using Java in the development and maintenance of application programs and systems.
Job Description for Engineer III
Engineer III typically performs multiple engineering-related tasks in various assignments within the organization. Oversees the design, development, implementation, and analysis of technical products and systems. Being an Engineer III has broad knowledge of engineering procedures and assists in the resolution of complex problems. May guide and train less experienced engineers. Additionally, Engineer III requires a bachelor's degree of engineering. Typically reports to a supervisor or manager. The Engineer III contributes to moderately complex aspects of a project. Work is generally independent and collaborative in nature. To be an Engineer III typically requires 4 to 7 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Engineer III information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Engineer III job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Engineer III
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Engineer III, the first career path typically starts with an Aeronautical Engineer IV position, and then Aeronautical Engineer V.
The second career path typically starts with an Aerospace Engineer IV position, and then progresses to Aerospace Engineer V.
The third career path typically starts with an Engineer IV position, and then progresses to Engineer V.
Additionally, the fourth career path typically starts with a Nuclear Engineer IV position, and then progresses to Nuclear Engineer V.
What does an Engineer III do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Engineer III Pay Difference by Location
Engineer III salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Engineer III, the highest Engineer III salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Engineer III salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Engineer III salary is in Miami, FL, where the Engineer III salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Engineer III

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Chemical Process Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Civil Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Cost Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title DevOps Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Facilities Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Engineer III
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Engineer III salary of your education level.
Engineer III Salary by Global Country
Engineer III salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Engineer III salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Engineer III salary of the other country.
Engineer III Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Engineer III salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Engineering Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Engineer III
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Engineer III salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Engineer III salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for an Engineer III, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Engineer III: Computer Simulation, Mathematical Modeling, Design Review, Design Optimization ...More
Recently searched related titles: City Engineer, Operations Engineer, Welding Engineer
Recently searched companies with related titles : Google, Inc. Staff Engineer, U.S. Navy Naval Engineer, Union Pacific Railroad Engineer
Recently searched related titles: Engineering Professional, Senior Staff Engineer, Engineering Associate
Jobs with a similar salary range to Engineer III : Corporate Operations Engineer, Quality Engineer III, Senior Stress Engineer, PAD Engineer, Paint Engineer, Senior PLANNING ENGINEER
Salary estimation for Engineer III at companies like : JDM FOOD GROUP Inc, Boston , New Hampshire & Maine, Massillon Senior Citizens Center
Jobs with a similar salary range to Engineer III : Custodian Engineer, Plan Reviewer, Ci Engineer