Field Operator II Salary in the United States
Field Operator II Salary
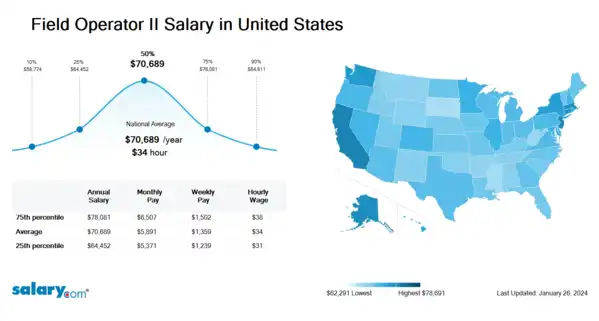
How much does a Field Operator II make in the United States? The average Field Operator II salary in the United States is $73,174 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $66,518 and $80,608. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Field Operator II Salary | $60,458 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Field Operator II Salary | $66,518 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Field Operator II Salary | $73,174 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Field Operator II Salary | $80,608 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Field Operator II Salary | $87,377 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Field Operator II need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Customer Service: Customer service is the provision of service to customers before, during and after a purchase. The perception of success of such interactions is dependent on employees "who can adjust themselves to the personality of the guest". Customer service concerns the priority an organization assigns to customer service relative to components such as product innovation and pricing. In this sense, an organization that values good customer service may spend more money in training employees than the average organization or may proactively interview customers for feedback. From the point of view of an overall sales process engineering effort, customer service plays an important role in an organization's ability to generate income and revenue. From that perspective, customer service should be included as part of an overall approach to systematic improvement. One good customer service experience can change the entire perception a customer holds towards the organization.
Pneumatics: Pneumatics (pronounced new-MATT-ix) is an aspect of physics and engineering that is concerned with using the energy in compressed gas to make something move or work.
HVAC: Designing, developing, maintaining, and updating Heating, Ventilation, Air-conditioning and Cooling system.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Field Operator II
Field Operator II sets up and operates a variety of oil, gas, or mining machines and equipment on designated sites. Reads and interprets blueprints and diagrams to select, operate, and properly secure machinery. Being a Field Operator II maintains equipment and troubleshoots technical issues as necessary. Routinely monitors and tests equipment for quality and safety in accordance with established procedures, guidelines, and regulations. Additionally, Field Operator II requires a high school diploma. Typically reports to a supervisor. The Field Operator II works under moderate supervision. Gaining or has attained full proficiency in a specific area of discipline. To be a Field Operator II typically requires 1-3 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Field Operator II.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Field Operator II information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Field Operator II job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Field Operator II
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Field Operator II, the first career path typically starts with a Field Service Technician III position, and then Field Service Supervisor.
The second career path typically starts with an Electro/Mechanical Technician III position, and then progresses to Electro/Mechanical Technician IV.
The third career path typically progresses to Power Systems Rental Operations Manager.
Additionally, the fourth career path typically starts with a Field Operator III position, and then progresses to Field Operations Supervisor.
What does a Field Operator II do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Field Operator II Pay Difference by Location
Field Operator II salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Field Operator II, the highest Field Operator II salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Field Operator II salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Field Operator II salary is in Miami, FL, where the Field Operator II salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Field Operator II

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Chemical Plant Operator II | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Computer Operator II | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationAssociates | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Desktop Publishing Operator II | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationAssociates | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Field Service Engineer II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Field Service Technician II | Experience 1 - 3 | EducationHigh School | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Field Operator II
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Field Operator II salary of your education level.
- Field Operator II Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Field Operator II Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Field Operator II Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Field Operator II Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Field Operator II Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Field Operator II Salary by Global Country
Field Operator II salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Field Operator II salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Field Operator II salary of the other country.
Field Operator II Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Field Operator II salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Skilled and Trades Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Field Operator II
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Field Operator II salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Field Operator II salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Field Operator II, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Field Operator II: Technical Services, Field Operations, Service Delivery, On Site Preventive Maintenance ...More
Recently searched related titles: Field Operations Specialist, Music Agent, Hospital Operator
Jobs with a similar salary range to Field Operator II : Operator II, Operator, Entry, Multi-Skilled Operator
Salary estimation for Field Operator II at companies like : Mitsubishi, LWML Kansas District Convention, Sumter
Jobs with a similar salary range to Field Operator II : Plastic Injection Mold Designer