Shipping Operations Manager Salary in the United States
Shipping Operations Manager Salary
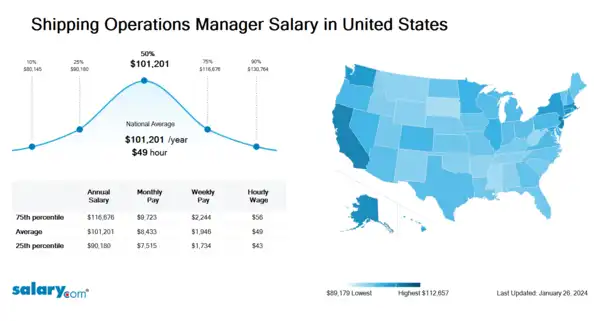
How much does a Shipping Operations Manager make in the United States? The average Shipping Operations Manager salary in the United States is $102,531 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $91,363 and $118,205. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Shipping Operations Manager Salary | $81,196 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Shipping Operations Manager Salary | $91,363 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Shipping Operations Manager Salary | $102,531 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Shipping Operations Manager Salary | $118,205 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Shipping Operations Manager Salary | $132,476 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Shipping Operations Manager need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Leadership: Knowledge of and ability to employ effective strategies that motivate and guide other members within our business to achieve optimum results.
Continuous Improvement: A continual improvement process, also often called a continuous improvement process (abbreviated as CIP or CI), is an ongoing effort to improve products, services, or processes. These efforts can seek "incremental" improvement over time or "breakthrough" improvement all at once. Delivery (customer valued) processes are constantly evaluated and improved in the light of their efficiency, effectiveness and flexibility. Some see CIPs as a meta-process for most management systems (such as business process management, quality management, project management, and program management). W. Edwards Deming, a pioneer of the field, saw it as part of the 'system' whereby feedback from the process and customer were evaluated against organisational goals. The fact that it can be called a management process does not mean that it needs to be executed by 'management'; but rather merely that it makes decisions about the implementation of the delivery process and the design of the delivery process itself.
Purchasing: Purchasing refers to a business or organization attempting to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations. Typically the word “purchasing” is not used interchangeably with the word “procurement”, since procurement typically includes expediting, supplier quality, and transportation and logistics (T&L) in addition to purchasing.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Shipping Operations Manager
Shipping Operations Manager manages shipping operations' daily activities, including order processing, inventory tracking, documentation, and transportation oversight. Utilizes enterprise resource planning (ERP) or other systems to record and track all shipping transactions, analyze performance metrics, and generate reports. Being a Shipping Operations Manager ensures shipping protocols and documentation meet required regulatory requirements for hazardous materials (DOT/HAZMAT) or special handling. Investigates and resolves shipping quality issues, damages, or lost freight claims. Additionally, Shipping Operations Manager develops and maintains relationships with carriers, freight forwarders, and vendors. May require a bachelor's degree or equivalent. Typically reports to a head of a unit/department. The Shipping Operations Manager manages subordinate staff in the day-to-day performance of their jobs. True first level manager. Ensures that project/department milestones/goals are met and adhering to approved budgets. Has full authority for personnel actions. To be a Shipping Operations Manager typically requires 5 years experience in the related area as an individual contributor. 1 - 3 years supervisory experience may be required. Extensive knowledge of the function and department processes. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Shipping Operations Manager.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Shipping Operations Manager information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Shipping Operations Manager job openings or enter a new job title here.
What does a Shipping Operations Manager do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Shipping Operations Manager Pay Difference by Location
Shipping Operations Manager salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Shipping Operations Manager, the highest Shipping Operations Manager salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Shipping Operations Manager salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Shipping Operations Manager salary is in Miami, FL, where the Shipping Operations Manager salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Shipping Operations Manager

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Branch Sales and Operations Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Computer Operations Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Enterprise Operations Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title HR Operations Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title HR Operations Senior Manager | Experience | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Shipping Operations Manager
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Shipping Operations Manager salary of your education level.
- Shipping Operations Manager Salaries with No Diploma
- Shipping Operations Manager Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Shipping Operations Manager Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Shipping Operations Manager Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Shipping Operations Manager Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Shipping Operations Manager Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Shipping Operations Manager Salary by Global Country
Shipping Operations Manager salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Shipping Operations Manager salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Shipping Operations Manager salary of the other country.
Shipping Operations Manager Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Shipping Operations Manager salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Materials Management Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Shipping Operations Manager
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Shipping Operations Manager salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Shipping Operations Manager salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Shipping Operations Manager, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Shipping Operations Manager: DOT Regulations, Delivery Management, Transit/Customs Documentation, Vendor Relationships ...More
Recently searched related titles: Air Freight Manager, Logistics Broker, Assistant Shipping Manager
Jobs with a similar salary range to Shipping Operations Manager : Truck Broker, Operations Chief
Salary estimation for Shipping Operations Manager at companies like : Anchor Products Services, ELDEE ASSOCIATES SUBSIDIARY Inc, 32 Industrial Ct LLC
Jobs with a similar salary range to Shipping Operations Manager : Shipping Team Leader, Shipping Inspector