Telecommunications Technician III Salary in the United States
Telecommunications Technician III Salary
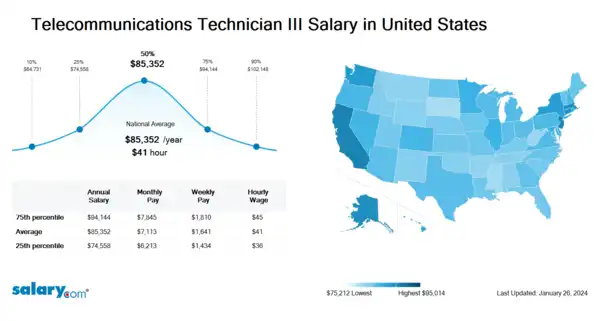
How much does a Telecommunications Technician III make in the United States? The average Telecommunications Technician III salary in the United States is $85,479 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $74,828 and $94,078. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Telecommunications Technician III Salary | $65,131 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Telecommunications Technician III Salary | $74,828 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Telecommunications Technician III Salary | $85,479 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Telecommunications Technician III Salary | $94,078 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Telecommunications Technician III Salary | $101,907 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Telecommunications Technician III need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Troubleshooting: Troubleshooting is a form of problem solving, often applied to repair failed products or processes on a machine or a system. It is a logical, systematic search for the source of a problem in order to solve it, and make the product or process operational again. Troubleshooting is needed to identify the symptoms. Determining the most likely cause is a process of elimination—eliminating potential causes of a problem. Finally, troubleshooting requires confirmation that the solution restores the product or process to its working state. In general, troubleshooting is the identification or diagnosis of "trouble" in the management flow of a system caused by a failure of some kind. The problem is initially described as symptoms of malfunction, and troubleshooting is the process of determining and remedying the causes of these symptoms. A system can be described in terms of its expected, desired or intended behavior (usually, for artificial systems, its purpose). Events or inputs to the system are expected to generate specific results or outputs. (For example, selecting the "print" option from various computer applications is intended to result in a hardcopy emerging from some specific device). Any unexpected or undesirable behavior is a symptom. Troubleshooting is the process of isolating the specific cause or causes of the symptom. Frequently the symptom is a failure of the product or process to produce any results. (Nothing was printed, for example). Corrective action can then be taken to prevent further failures of a similar kind.
Network Solutions: Network Solutions offers everything you need to get online quickly. From website development to optimization, social media, online advertising and more, we'll have your business online in no time.
Wireless Network: Wireless networks are computer networks that are not connected by cables of any kind. The use of a wireless network enables enterprises
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Telecommunications Technician III
Telecommunications Technician III maintains an organization's telecommunications network to ensure dependable operation. Monitors network systems and performs diagnostic tests to document and report performance levels. Being a Telecommunications Technician III conducts routine checks and preventative maintenance to minimize malfunctions and downtime. Troubleshoots telecommunication issues and performs or coordinates repairs. Additionally, Telecommunications Technician III may require an associate degree. Typically reports to a supervisor. The Telecommunications Technician III works independently within established procedures associated with the specific job function. Has gained proficiency in multiple competencies relevant to the job. To be a Telecommunications Technician III typically requires 3-5 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Telecommunications Technician III.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Telecommunications Technician III information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Telecommunications Technician III job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Telecommunications Technician III
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Telecommunications Technician III, the upper level is Telecommunications Supervisor I and then progresses to Telecommunications Supervisor II.
What does a Telecommunications Technician III do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Telecommunications Technician III Pay Difference by Location
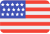
Telecommunications Technician III salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Telecommunications Technician III, the highest Telecommunications Technician III salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Telecommunications Technician III salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Telecommunications Technician III salary is in Miami, FL, where the Telecommunications Technician III salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Telecommunications Technician III

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Telecommunications Analyst I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Telecommunications Analyst II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Telecommunications Analyst III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Telecommunications Analyst IV | Experience 7 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Telecommunications Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Telecommunications Technician III
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Telecommunications Technician III salary of your education level.
- Telecommunications Technician III Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Telecommunications Technician III Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Telecommunications Technician III Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Telecommunications Technician III Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Telecommunications Technician III Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Telecommunications Technician III Salary by Global Country
Telecommunications Technician III salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Telecommunications Technician III salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Telecommunications Technician III salary of the other country.
Telecommunications Technician III Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Telecommunications Technician III salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All IT - All Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Telecommunications Technician III
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Telecommunications Technician III salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Telecommunications Technician III salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Telecommunications Technician III, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Telecommunications Technician III: System Monitoring, IT Network Software, VoIP Software, Telephony ...More
Recently searched related titles: Avionics Test Engineer, Data Communications Technician, Tower Technician
Jobs with a similar salary range to Telecommunications Technician III : Sector Manager, Robotics and Automation Technician, Communications Technician
Salary estimation for Telecommunications Technician III at companies like : Turnstone Emergency Physicians LLC, Medical College Of Pennsylvania, Roane County Register
Jobs with a similar salary range to Telecommunications Technician III : Radio Tech