Reliability Engineer III Salary in the United States
Reliability Engineer III Salary
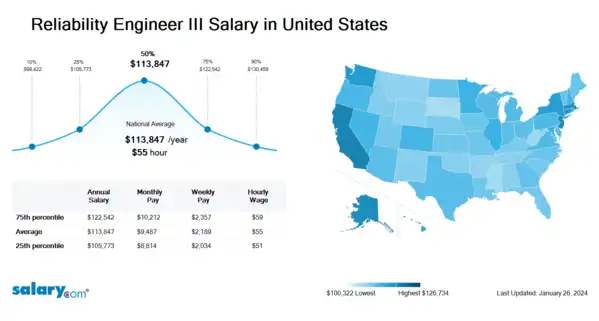
How much does a Reliability Engineer III make in the United States? The average Reliability Engineer III salary in the United States is $114,526 as of March 26, 2024, but the range typically falls between $106,406 and $123,272. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Reliability Engineer III Salary | $99,012 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Reliability Engineer III Salary | $106,406 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Reliability Engineer III Salary | $114,526 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Reliability Engineer III Salary | $123,272 | US | March 26, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Reliability Engineer III Salary | $131,234 | US | March 26, 2024 |
Corporate One FCU - Columbus, OH
ComResource - Columbus, OH
Maven - Columbus, OH
Senior Engineer Transmission Modeling
American Municipal Power, Inc - Columbus, OH
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Reliability Engineer III need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Analysis: Analysis is the process of considering something carefully or using statistical methods in order to understand it or explain it.
Container: Container is an object used for or capable of holding, esp for transport or storage, such as a carton, box, etc.
Software Engineering: Software engineering is the application of engineering to the development of software in a systematic method. Notable definitions of software engineering include: "the systematic application of scientific and technological knowledge, methods, and experience to the design, implementation, testing, and documentation of software"—The Bureau of Labor Statistics—IEEE Systems and software engineering - Vocabulary "The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software"—IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology "an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production"—Ian Sommerville "the establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to economically obtain software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines"—Fritz Bauer
Job Description for Reliability Engineer III
Reliability Engineer III analyzes and evaluates the reliability of products, equipment, components, and processes using engineering methodologies and tools. Develops the methods and measures utilized for reliability analysis based on product specifications, tolerances, or operating standards. Being a Reliability Engineer III utilizes analysis techniques like FMEA, fault tree, and root cause analysis to identify problems. Oversees testing activities and reviews results. Additionally, Reliability Engineer III creates risk-based failure mitigation plans. Proposes new or revised product designs, manufacturing processes and testing specifications that utilize best practices and will increase reliability. Requires a bachelor's degree in engineering. Typically reports to an engineering manager. The Reliability Engineer III work is generally independent and collaborative in nature. Contributes to moderately complex aspects of a project. To be a Reliability Engineer III typically requires 4-7 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Reliability Engineer III.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Reliability Engineer III information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Reliability Engineer III job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Reliability Engineer III
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Reliability Engineer III, the first career path typically starts with a Corrosion Engineer III position, and then progresses to Corrosion Maintenance Supervisor.
Additionally, the second career path typically starts with a Reliability Engineer IV position, and then progresses to Reliability Engineer V.
What does a Reliability Engineer III do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Reliability Engineer III Pay Difference by Location
Reliability Engineer III salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Reliability Engineer III, the highest Reliability Engineer III salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Reliability Engineer III salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Reliability Engineer III salary is in Miami, FL, where the Reliability Engineer III salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Reliability Engineer III

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Electrical Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Integrated Solutions Engineer III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Reliability Engineer I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Reliability Engineer II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Reliability Engineer III
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Reliability Engineer III salary of your education level.
Reliability Engineer III Salary by Global Country
Reliability Engineer III salary varies from country to country. There are several factors that mainly impact the Reliability Engineer III salary, including cost of living, economic conditions, market rates and legal differences. Click below to Reliability Engineer III salary of the other country.
Reliability Engineer III Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Reliability Engineer III salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Engineering Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Reliability Engineer III
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Reliability Engineer III salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Reliability Engineer III salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Reliability Engineer III, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Reliability Engineer III: Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) Software, Root Cause Analysis, Computer Simulation, Reliability Analysis ...More
Recently searched related titles: Senior Site Reliability Engineer
Jobs with a similar salary range to Reliability Engineer III : Asset Integrity Engineer, Quantitative Analysis, Maintenance Reliability Engineer
Salary estimation for Reliability Engineer III at companies like : Seahorse Key Marine Laboratory, Salon Andres, Sentinel Holdings LLC
Jobs with a similar salary range to Reliability Engineer III : Reliability Specialist, Lead Sre, Reliability Coordinator