Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary in the United States
Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary
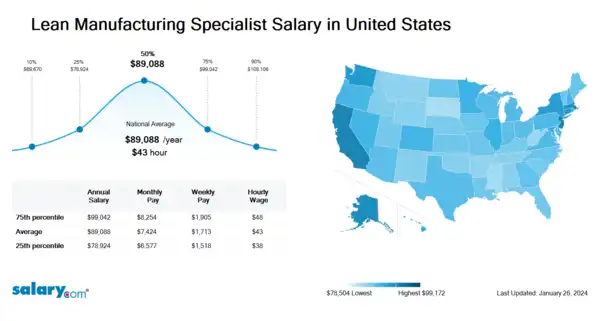
How much does a Lean Manufacturing Specialist make in the United States? The average Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary in the United States is $90,333 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $80,027 and $100,429. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary | $70,643 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary | $80,027 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary | $90,333 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary | $100,429 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary | $109,621 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does a Lean Manufacturing Specialist need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Problem Solving: Analyzing and identifying the root cause of problems and applying critical thinking skills to solve problems.
Lean Six Sigma: Applying the methods of Lean Six Sigma in reducing variation, waste, and cycle time to achieve customer satisfaction and bottom-line results.
Root Cause Analysis: In science and engineering, root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving used for identifying the root causes of faults or problems. It is widely used in IT operations, telecommunications, industrial process control, accident analysis (e.g., in aviation, rail transport, or nuclear plants), medicine (for medical diagnosis), healthcare industry (e.g., for epidemiology), etc. RCA can be decomposed into four steps: Identify and describe clearly the problem. Establish a timeline from the normal situation up to the time the problem occurred. Distinguish between the root cause and other causal factors (e.g., using event correlation). Establish a causal graph between the root cause and the problem.RCA generally serves as input to a remediation process whereby corrective actions are taken to prevent the problem from reoccurring. The name of this process varies from one application domain to another.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for Lean Manufacturing Specialist
Lean Manufacturing Specialist assists with the implementation of Lean Manufacturing goals and strategies for improving the operations and processes within the organization. Evaluates all continuous improvement activities and implements plans to optimize performance and processes. Being a Lean Manufacturing Specialist employs Lean methodologies and tools in order to accomplish business objectives. Typically requires a bachelor's degree. Additionally, Lean Manufacturing Specialist also requires training and Lean certification through an accredited organization. Typically reports to a manager or head of a unit/department. To be a Lean Manufacturing Specialist typically requires 2 to 4 years of related experience. Gains exposure to some of the complex tasks within the job function. Occasionally directed in several aspects of the work. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
See user submitted job responsibilities for Lean Manufacturing Specialist.
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of Lean Manufacturing Specialist information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see Lean Manufacturing Specialist job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for Lean Manufacturing Specialist
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For Lean Manufacturing Specialist, the upper level is Lean Manufacturing Specialist, Sr. and then progresses to Lean Manufacturing Manager.
What does a Lean Manufacturing Specialist do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

Lean Manufacturing Specialist Pay Difference by Location
Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of Lean Manufacturing Specialist, the highest Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary is 25.0% above. The lowest Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary is in Miami, FL, where the Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to Lean Manufacturing Specialist

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Lean Manufacturing Manager | Experience 5 + | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Lean Manufacturing Specialist, Sr. | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Manufacturing Director | Experience | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Manufacturing Engineer I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Manufacturing Engineer II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for Lean Manufacturing Specialist
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary of your education level.
- Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salaries with No Diploma
- Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
Lean Manufacturing Specialist Salary by State
Geographic variations impact Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Manufacturing Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With Lean Manufacturing Specialist
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary varies from category to category. Click below to see Lean Manufacturing Specialist salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for a Lean Manufacturing Specialist, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with Lean Manufacturing Specialist: Manufacturing Fabrication, Process Improvement, Manufacturing Operations Management, ERP Systems ...More
Recently searched related titles: Lean Consultant
Recently searched related titles: Business Intelligence Solutions Analyst, MS BI Consultant, SCM Engineer
Jobs with a similar salary range to Lean Manufacturing Specialist : Continuous Improvement Consultant, Continuous Improvement Coordinator, Continuous Improvement Facilitator, Design Manufacturing Engineer, Lean Industrial Engineer, Lean Practitioner
Salary estimation for Lean Manufacturing Specialist at companies like : DMnpc international Inc, Tile Holdings LLC, Quantum Purposes Inc
Jobs with a similar salary range to Lean Manufacturing Specialist : Lean Six Sigma Specialist