RFP Analyst Salary in the United States
RFP Analyst Salary
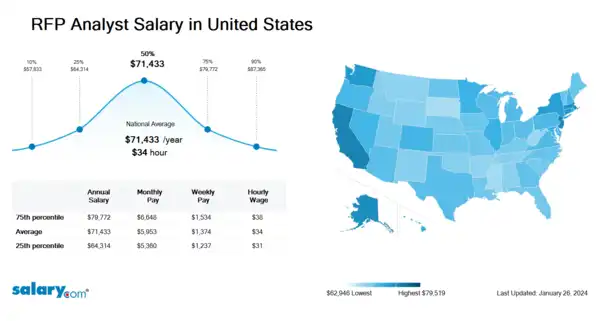
How much does an RFP Analyst make in the United States? The average RFP Analyst salary in the United States is $75,096 as of June 27, 2024, but the range typically falls between $67,466 and $83,655. Salary ranges can vary widely depending on many important factors, including education, certifications, additional skills, the number of years you have spent in your profession. With more online, real-time compensation data than any other website, Salary.com helps you determine your exact pay target.
| Percentile | Salary | Location | Last Updated |
| 10th Percentile RFP Analyst Salary | $60,520 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 25th Percentile RFP Analyst Salary | $67,466 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 50th Percentile RFP Analyst Salary | $75,096 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 75th Percentile RFP Analyst Salary | $83,655 | US | June 27, 2024 |
| 90th Percentile RFP Analyst Salary | $91,447 | US | June 27, 2024 |
- View Hourly Wages
-
Select State
-
Select City
-
Choose Similar Job
-
Pick Related Category
- View Cost of Living in Major Cities
What skills does an RFP Analyst need?
Each competency has five to ten behavioral assertions that can be observed, each with a corresponding performance level (from one to five) that is required for a particular job.
Analysis: Analysis is the process of considering something carefully or using statistical methods in order to understand it or explain it.
User Stories: In software development and product management, a user story is an informal, natural language description of one or more features of a software system. User stories are often written from the perspective of an end user or user of a system. They are often recorded on index cards, on Post-it notes, or in project management software. Depending on the project, user stories may be written by various stakeholders including clients, users, managers or development team members. User stories are a type of boundary object. They facilitate sensemaking and communication; that is, they help software teams organize their understanding of the system and its context. User stories are often confused with system requirements. A requirement is a formal description of need; a user story is an informal description of a feature.
Accounting: Creating financial statements and reports based on the summary of financial and business transactions.
What Should I Pay?

Job Description for RFP Analyst
RFP Analyst develops proposals, bids, quotations, RFP responses, or other documents describing organizational products and services in response to requests from prospective clients. Collaborates and coordinates with internal contributors and subject matter experts to ensure content is complete, accurate, and maximizes business opportunities. Being an RFP Analyst prepares and maintains a repository of templates, standard language, and product collateral or exhibits. May prepare custom response content for complex or unique inquiries. Additionally, RFP Analyst typically requires a bachelor's degree or equivalent. Typically reports to a manager or head of a unit/department. The RFP Analyst occasionally directed in several aspects of the work. Gaining exposure to some of the complex tasks within the job function. To be an RFP Analyst typically requires 2 -4 years of related experience. (Copyright 2024 Salary.com)... View full job description
Search Job Openings
Salary.com job board provides millions of RFP Analyst information for you to search for. Click on search button below to see RFP Analyst job openings or enter a new job title here.
Career Path for RFP Analyst
A career path is a sequence of jobs that leads to your short- and long-term career goals. Some follow a linear career path within one field, while others change fields periodically to achieve career or personal goals.
For RFP Analyst, the upper level is RFP Analyst, Sr. and then progresses to RFP Manager.
What does an RFP Analyst do?
Are you an HR manager or compensation specialist?
Salary.com's CompAnalyst platform offers:
- Detailed skills and competency reports for specific positions
- Job and employee pricing reports
- Compensation data tools, salary structures, surveys and benchmarks.

RFP Analyst Pay Difference by Location
RFP Analyst salary varies from city to city. Compared with national average salary of RFP Analyst, the highest RFP Analyst salary is in San Francisco, CA, where the RFP Analyst salary is 25.0% above. The lowest RFP Analyst salary is in Miami, FL, where the RFP Analyst salary is 3.5% lower than national average salary.
| City, State | Compared to national average |
|---|---|
| City, State San Francisco, CA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Washington, DC |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Miami, FL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Chicago, IL |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Boston, MA |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State New York, NY |
Compared to national average
|
| City, State Dallas, TX |
Compared to national average
|
Similar Jobs to RFP Analyst

| Job Title | Experience | EDUCATION | Salary Compared to This Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Title Billing Analyst II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Credit Analyst I | Experience 0 - 2 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Credit Analyst II | Experience 2 - 4 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title Credit Analyst III | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
| Job Title RFP Analyst, Sr. | Experience 4 - 7 | EducationBachelors | Salary Compared to This Job |
Level of Education for RFP Analyst
Jobs with different levels of education may pay very differently. Check the RFP Analyst salary of your education level.
- RFP Analyst Salaries with No Diploma
- RFP Analyst Salaries with a High School Diploma or Technical Certificate
- RFP Analyst Salaries with an Associate's Degree
- RFP Analyst Salaries with a Bachelor's Degree
- RFP Analyst Salaries with a Master's Degree or MBA
- RFP Analyst Salaries with a JD, MD, PhD or Equivalent
RFP Analyst Salary by State
Geographic variations impact RFP Analyst salary levels, due to various factors, such as cost of living, industries, market demand and company budgets. Click below to see pay differences between states.
Browse All Marketing Jobs by Salary Level
Browse Related Job Categories With RFP Analyst
A job category is a classification or grouping of job positions that share similar characteristics, functions, or industries. RFP Analyst salary varies from category to category. Click below to see RFP Analyst salary in different categories.
Take just three simple steps below to generate your own personalized salary report
Understand the total compensation opportunity for an RFP Analyst, base salary plus other pay elements
Average Base Salary
Core compensation
Average Total Cash Compensation
Includes base and annual incentives
View the Cost of Living in Major Cities
Skills associated with RFP Analyst: Proposal Management, Request For Proposal Management, Quote Management Software, RFP (Request For Proposal) ...More
Recently searched related titles: Talent Producer, Bid Analyst, Operations Analyst Goldman Sachs
Jobs with a similar salary range to RFP Analyst : Assistant Library Director, Bid Support Specialist, Bid Specialist, Project Business Analyst
Salary estimation for RFP Analyst at companies like : Professional Water Technology Inc, SunTrust Bank Private Wealth Management, Keene State College Film Society
Jobs with a similar salary range to RFP Analyst : Quote Specialist, Rfp Specialist