Incentive Pay: Definitions, Types & Examples for You

Incentive pay is an additional wage or salary payment given to employees over and above their base pay. The purpose of incentive pay is to encourage workers to put in more effort or accomplish particular objectives. It may come in profit-sharing payments, individual bonuses, or group bonuses. Employees who reach or surpass predetermined performance targets are rewarded through performance-based pay schemes, frequently combined with incentive compensation.

When Should You Start Incentive Pay?
To retain key staff, you may offer incentive pay to your senior management team or to your sales team when they reach specific milestones. To increase output and overall morale, you might think about providing all employees with incentive pay to all employees. However, if you do that, you'll need to decide under what conditions incentive pay will be granted.
An incentive pay plan must be carefully considered before being established in order to be rewarding and provide recognition. If sufficient transparency and thorough thinking are lacking, this kind of program may is a possibility that this kind of program will be demoralizing and polarizing.
Applying the SMART system (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-limited) is a fantastic idea to use the SMART method (specific, measurable, attainable, practical, and time-limited) when developing an incentive pay plan.
Types of Incentives Pay
Long-term and short-term incentive pay are two different forms of compensation that are used to incentivize employees based on different time horizons and goals.
- Short-term incentive pay:
Short-term incentive compensation is typically designed to reward immediate or near-term performance achievements. These incentives are tied to specific, short-term goals, such as quarterly or annual targets. Short-term incentive pay is often used to motivate and reward employees for meeting or exceeding performance expectations within a relatively short timeframe.
Examples of short-term incentives include performance bonuses, sales commissions, or other forms of variable pay that are directly tied to individual or team performance over a specific period. These incentives provide immediate financial rewards and are often based on quantitative metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the organization's short-term objectives.
-
Long-term incentive pay:
Long-term incentives are designed to align employee interests with the long-term success and sustainability of the organization. These incentives focus on rewarding employees for contributing to the company's growth, profitability, or other strategic objectives over an extended period.
Common long-term incentives include stock options, equity grants, or profit-sharing programs where employees receive a share of the company's profits or gains over time. These incentives aim to provide employees with a sense of ownership and an opportunity to benefit from the company's long-term success.
Long-term incentives often have vesting periods, meaning that employees must remain with the organization for a certain period before they are eligible to fully realize the benefits. This helps promote employee retention and long-term commitment to the organization's goals.
Both short-term and long-term incentive pay can be used in combination to provide a comprehensive compensation package that motivates employees in the short term while aligning their interests with the long-term success of the organization. The specific mix of short-term and long-term incentives will depend on the industry, organizational goals, and the desired balance between immediate performance and sustained growth.
How to Implement an Incentive Pay System:
To effectively use incentive pay, it is important to develop a well-designed program that aligns with your organization's goals and motivates employees to perform at their best. Here are some steps to consider when implementing an incentive pay system:
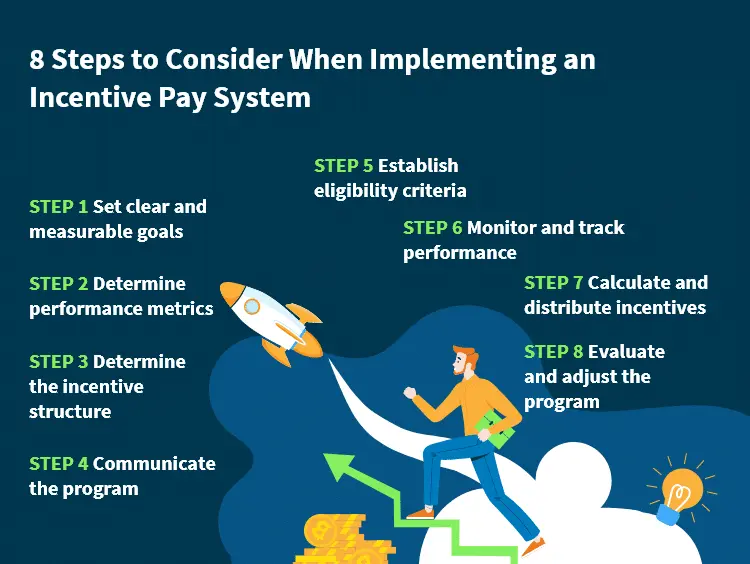
- Set clear and measurable goals: Clearly define the objectives that you want to incentivize. Ensure that the goals are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). This will provide employees with a clear target to strive for.
- Determine performance metrics: Identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure employee performance. These metrics should be directly connected to the goals you have set. Make sure they are objective, fair, and easily measurable.
- Determine the incentive structure: Decide on the type of incentive you will offer, whether it's performance bonuses, commissions, profit sharing, stock options, or a combination of these. Consider the financial resources available to allocate to incentives and ensure that the structure is affordable and sustainable.
- Communicate the program: Clearly communicate the incentive program to all employees. Explain the goals, metrics, and eligibility criteria. Ensure employees understand how their performance will be measured and how the incentives will be calculated. Transparency is crucial to gaining employee buy-in and trust.
- Establish eligibility criteria: Determine which employees or teams will be eligible for the incentive program. This could be based on job roles, departments, or performance thresholds. Ensure that the criteria are fair and non-discriminatory.
- Monitor and track performance: Continuously monitor and track employee performance against the established metrics. Provide regular feedback to employees on their progress and performance. This will enable them to understand where they stand in relation to their goals and make necessary adjustments.
- Calculate and distribute incentives: Once the performance period is completed, calculate the incentives based on the predetermined formula. Make sure the calculation process is transparent and accurate. Distribute the incentives promptly and communicate the results to employees.
- Evaluate and adjust the program: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the incentive program. Analyze its impact on employee motivation, performance, and overall organizational goals. Modify and refine the program as needed to ensure it remains aligned with changing business needs and employee expectations.
Remember, the success of an incentive compensation program depends on its design, communication, fairness, and alignment with organizational goals. Regularly review and adapt the program to ensure it continues to drive desired employee behavior and performance.
Is Incentive Pay Genuinely Adequate?
Indeed, incentive pay is adequate, mainly when a perceived lack of benefits exists. It is more likely to be seen as guaranteed pay if incentive pay is consistently provided.
The advantages of incentive compensation can help you to grasp better why.
Rewards for Incentive Pay
A well-thought-out incentive compensation plan should advance both your company and its workforce. Pay incentives:
- Harmonizes vendor, partner, and employee interests with business objectives
- Specifies the priorities for your company.
- Encourages employees to enhance procedures and frameworks to meet their objectives.
- Gives prizes to achievers
- Fosters a culture of performance and teamwork
- Presses workers to keep improving their abilities in order to meet objectives
- Intellectual and professional stimulation can lower employee turnover.
All of the aforementioned factors lead to an enhanced customer experience and a better product or service. Ultimately, these gains in productivity and efficiency translate into real top-and bottom-line growth.
Key Conclusions
Merit-based pay is what incentive pay is. It can take the shape of monetary or non-monetary awards and is typically linked to performance or reaching predetermined goals.
Insights You Need to Get It Right







